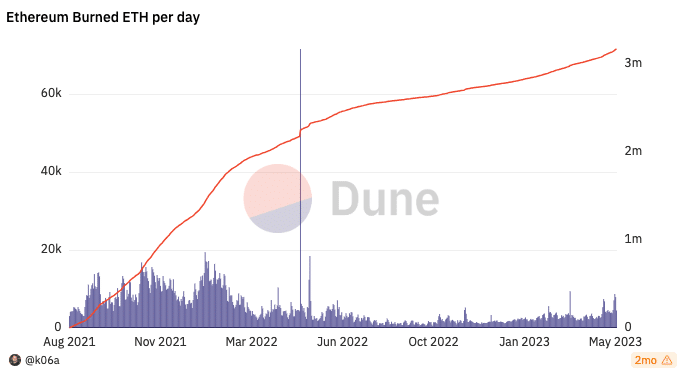
- The value of ETH burned since 2021 approached $10 billion.
- Gas usage on the Ethereum network dropped due to low activity.
Since the implementation of Ethereum Improvement Proposal 1559 (EIP-1559), an upgrade aimed at improving the network’s transaction fee mechanism, Ethereum [ETH] has witnessed a significant amount of ETH being burned.
Read Ethereum’s [ETH] Price Prediction 2023-2024
The mechanism, which reduces the supply of ETH, has resulted in the burning of nearly $10 billion worth of ETH tokens, Dune Analytics revealed.

Source: Dune Analytics
Coping with the hope
Implemented in August 2021, the Ethereum team developed EIP-1559 as one of the London Hark Fork Improvement Proposals. This happened alongside EIP-3554, 3198, 3529, and EIP-3541.
All these developments happened in preparation for its transition to Proof-of-Stake (PoS). For EIP-1559, the objective was to get rid of the previous fee market mechanism relating to its main gas fee calculation.
While many users had hoped that the development would reduce gas fees on the network, it didn’t. Instead, it brought about a discrete base fee, aimed at prioritizing transactions when validating blocks.
Further information from Dune, the analytics platforms showed that projects like Uniswap [UNI], Circle [USDC], and NFT marketplace OpenSea, played vital roles in the increase.
At press time, nearly 300,00 ETH each had been burned via Uniswap and OpenSea. And the reason for this is clear. Uniswap maintained its position as the leading Decentralized Exchange (DEX).
So, a lot of ETH swaps with other tokens influenced its rise. For OpenSea, its place as the number on the Ethereum-based marketplace puts it in the aforementioned positions. As for USDC, its position as the favored stablecoin in DEXes helped up its rank.

Source: Dune Analytics
Gas usage falls
However, Ethereum gas used had decreased as of this writing. According to Santiment, the ETH gas used was 16.05 billion. Used gas usage spikes when there’s a lot of activity on the network.
And this demand for ETH causes a rise in gas prices. So, the fall in usage reflects a relatively less busy period for the Ethereum network.
On looking at the network growth, the on-chain data provider revealed that the metric had decreased sharply. Typically, network growth measures the rate of adoption and influx of new users into a network.
So, when the network growth increases, it means that a project has impressive traction. However, when the metric decreases, it implies that utilization is low. And this is usually accompanied by low liquidity.
![Ethereum [ETH] gas used and network growth](https://statics.ambcrypto.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Ethereum-ETH-12.45.52-17-Jul-2023.png)
Source: Santiment
In conclusion, Ethereum’s burn mechanism has relatively addressed the network’s concerns around transaction fees.
Also, the substantial amount of ETH burned also demonstrates the demand and usage of the Ethereum network, as well as the effectiveness of creating a more deflationary ecosystem. Whether it will improve or not, time will tell.